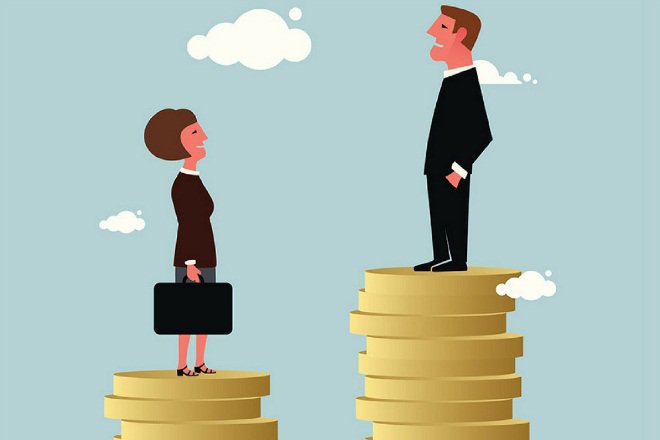
India celebrated Women’s Day 2019 with corporate chains and online shopping websites giving out huge discounts on their products. However, we often forget the history and the context in which the day is celebrated; a day that primarily came into being with the spirit of women struggling for their basic rights. On the 108th International Working Women’s Day, where do the working class women of India stand? How often do we talk about the unpaid work that women continue to do, which sustains the economy and never gets accounted for? How far have we progressed in terms of equal pay for women’s labor?
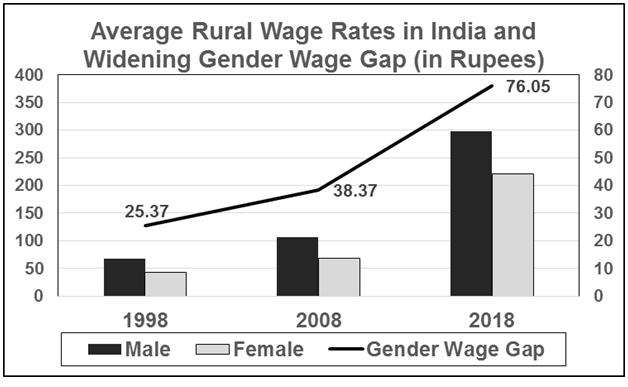
When we look at the average wage rate of various rural agricultural and non-agricultural occupations for the months of December in 1998, 2008 and 2018, for male and female workers in India, the prevalence of a widening gender wage-gap becomes evident. While calculating the average rural wage rates, we have considered wages for activities like ploughing, tilling, sowing, harvesting, picking, horticulture, fishing, wood-cutting, animal husbandry, packaging, plant protection, carpentry, blacksmithing, cobbling, masonry, weaving, beedi-making, bamboo and cane basket making, handicrafts, plumbing, electrician work, construction work, LMV and tractor driving, sweeping, cleaning, and other agricultural and non-agricultural activities (from the Labour Bureau, GoI).
The average male wage rate increased from Rs. 68 in 1998 to Rs. 107 in 2008, further to Rs. 297.50 in 2018. The average female wage rate, on the other hand, has become Rs. 221.50 in 2018 from Rs. 68.50 in 2008 and Rs. 43 in 1998. In the last 10 years, the gender wage-gap on an average has gone up from Rs. 38 to Rs. 76 (almost doubled!). In the period between 1998 and 2008, the gender wage-gap had gone up from Rs. 25 to Rs. 38, registering an increase of more than 50 per cent in absolute terms. However, in relative terms, the gender wage-gap has come down during the last 10 years as compared to the previous decade. But the sheer fact that the gender wage-gap still exists and that the average female wage rate is still less than 3/4th of average male wage rate in rural India is a matter of grave concern.
This article first appeared on Newsclick