In the Philippines, the cost of living crisis in the country is expressed, on the one hand, in the deflation of real wages and, on the other hand, in the shrinkflation of commodities. Caught between shrinking amounts of products and shrinking value of wages, workers are reeling from hardship during the holidays. No wonder that a survey has shown that one of every four employees prefer to monetize the Christmas parties held by companies for their workforce. It is better to have money in their pockets than to have fun with workmates.
In 14 out of 17 regions, minimum wages were increased by PHP 30 to PHP 40 in the second half of this year, bringing them to a high of PHP 610 in Metro Manila, and to a low of PHP 368 in the Zamboanga Peninsula. However, the equivalent real wages remain depressed. The real wage in Metro Manila is only PHP 504. That is, PHP 610 in 2023 can only buy the equivalent of PHP 504 in 2018, indicating a gap of PHP 106. [The exchange at the moment is about USD 1 to PhP 55]
The difference between nominal and real wages is a result of inflation over the years: wage hikes have not kept up with the rise in prices and so workers’ purchasing power has been depleted. The nominal versus real wage gap ranges from PHP 63 in Zamboanga Peninsula to PHP 108 in Central Luzon. Thus there is the necessity for Congress to plug the gap by enacting the bill for a PHP 150 salary increase.
The minimum wage adjustments were a belated response from the government to organized labor’s demand for salary increases since last year. In December 2022, the group Kapatiran ng mga Unyon at Samahang Manggagawa filed a petition for an additional PHP 100 minimum wage so that workers can recover their lost purchasing power. Similar petitions were filed in Calabarzon, Cebu and Western Visayas. The wage orders from the different regional wage boards then fell short of the wage recovery demand. Expectedly, real wages stayed deflated despite the latest round of minimum wage hikes.
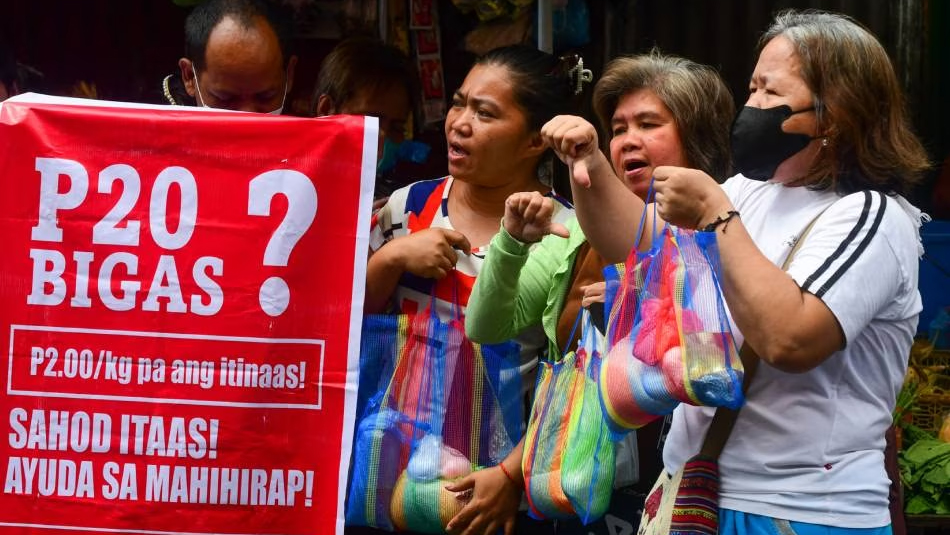
Shrinkflation is just one problem facing workers and the poor. Rice cannot shrink and so its price continues to rise. One kilo of rice today costs between PHP 52 and PHP 68. The onset of El Nino next year is bound to raise the price of rice even more. As a pre-emptive move, President Bong Bong Marcos Jr. has already extended the tariff cut on imported rice up to the end of next year to ease rice inflation. Still, this is a band aid solution. His election promise to bring the cost of rice to PHP 20 per kilo is even further from reality.
Food in general remains the biggest expenditure for ordinary households. This reveals not just the survival challenges for the working class but the underdevelopment problem faced by Philippine society. Higher expenses for non-food items are a characteristic of more developed countries.
Reality of jeepney livelihood loss versus the myth of new jobs created
In a year end statement, the government asserted that 200,000 new jobs were created as a result of investment pledges accruing from President Bong Bong Marcos’ trips abroad. Assuming this is true—the government needs to explain how they guessed these figures—this is almost matched by the number of traditional jeepney operators and drivers who will lose their livelihood as a result of the cancellation of their individual franchises. The President does not need a 58% hike in his travel budget to PHP 1.4 billion to generate new jobs, he just needs to extend the individual franchises so that existing livelihoods are preserved.
Jeepneys are the ubiquitous means of public transport in the country. Almost all operators own just one jeepney unit and hire drivers on an informal arrangement on those days that they will not ply their vehicles themselves. Jeepney operators and drivers are among the working poor.
At the stroke of midnight on December 31, 144,000 will lose their livelihoods. This is conservatively estimated as one operator and one driver for the 74,000 jeepneys units which have not been consolidated either into cooperatives or corporations, according to the Land Transportation and Franchising Board. This is a significant number, comprising an additional 7% to the 2,090,000 officially unemployed Filipinos as of October 2023.
The current administration is just implementing a business-as-usual and hands-off approach to employment: let the private sector, whether local or foreign, direct economic development. In place for 50 years or so, this broken system has led us to double-digit unemployment plus underemployment and permanent overseas migration.
It is high time to contemplate another and better way: an industrial and agricultural policy that focuses on job creation. This should be at the top of the wish list for 2024.
While unemployment in October has gone down to 4.2%, underemployment is more than double that at 11.7%. The underemployed are those who want more hours of work, presumably because they do not earn enough. This is a result of the very broad definition of an employed person—somebody who has worked for at least one hour in the previous week. No wonder there is very low official unemployment.
Another statistic that reveals the extent of the problem of lack of quality jobs is the high rate of migration. The latest figures from the Philippine Statistics Authority show that almost two million Filipinos worked abroad annually or some 5,000 OFWs were deployed daily. This sums up to about 2.6% of the total population that is over 15 years old. In other words, the unemployment rate would go up by more than half, at the very least to 6.8%, if Filipinos did not leave for gainful employment abroad.
Slightly more than half of Filipino migrant workers are female and more than one fourth of them—the largest cohort—are young workers aged 30 to 34 years. An overwhelming number of OFWs are in the elementary occupations, a euphemism for unskilled and menial jobs such as domestic and care work, and construction jobs. Meaning, Filipinos are working abroad not for dream jobs but for 3D work—dirty, dangerous and demeaning—that just happens to pay better than what is available in the country. Again to stress the point, the Philippine migration profile exposes the open secret of the deficits of good-paying jobs in the country.
The father of Susan Ople—Secretary of the Department of Migrant Workers (DMW) who died this year—was Blas Ople who, as then Labor Minister, presided over a temporary program to place Filipino workers in the Middle East in 1976. It was deemed provisional since it was a disgrace for the dictator Ferdinand Marcos Sr. to admit that workers had to be deployed abroad to ease unemployment in the country. A temporary scheme that has lasted 47 years from two fathers, Ferdinand Marcos Sr. and Blas Ople, to their children, Bong Bong Marcos Jr. and Susan Ople, is a testament to the utter bankruptcy of the economic and employment models followed by all the past governments, whether before or after the democratic transition in 1986. The establishment of the DMW is a tacit admission that the government considers migration to be a permanent not provisional system to create jobs for Filipinos.
Judy Ann Miranda is secretary general of Partido Manggagawa (PM) and a board member of Women’s Day Off, an NGO.
Rene Magtubo is chair of PM and an elected councilor in one of the cities of Metro Manila.